Disclaimer: This article is provided for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal or tax advice. The information contained herein may not be applicable in all situations or jurisdictions, and readers are encouraged to consult with their own legal or tax professionals for advice specific to their circumstances.
In today’s digital-first world, remote work and virtual meetings are integral to personal and professional interactions. Tools that record meetings, transcribe conversations, and produce automated summaries are widely available and can significantly enhance productivity. However, with this ease comes a central question: is it illegal to record someone without their permission?
Understanding the legal framework around recording conversations, as well as the ethical implications, is essential when using AI-powered meeting tools. In this article, we’ll explore the laws governing recording, discuss ethical considerations, and provide guidance on responsibly using AI meeting tools like Krisp.
Understanding Recording Laws: One-Party vs. Two-Party Consent
Before hitting “record,” it’s essential to understand that recording laws vary widely by jurisdiction, and recording someone without consent can have serious legal implications. Broadly speaking, jurisdictions fall into two categories regarding recording laws: one-party consent and two-party (or all-party) consent.
One-Party Consent Laws
In jurisdictions with one-party consent laws, only one participant in the conversation needs to consent to the recording. This means that, for example, if you are in a Zoom meeting, you can record the conversation without informing other participants. In the United States, around 38 states follow one-party consent rules. This approach provides more flexibility, enabling recordings in professional settings to document discussions or capture key points without needing explicit approval from each participant.
However, ethical considerations remain even if one-party consent legally allows recording without informing others. In business settings, it’s generally best to inform participants if a meeting is being recorded to foster trust and prevent misunderstandings.
Two-Party (or All-Party) Consent Laws
Two-party consent laws require that all individuals involved in a conversation agree to be recorded, following stricter guidelines to protect privacy. States like California, Florida, and Illinois in the U.S., along with countries like Germany and several others in the EU, enforce this requirement. Recording someone without their knowledge or consent in these jurisdictions is illegal and can result in serious consequences, including fines and potential criminal charges.
In regions with two-party consent laws, it is crucial to ensure that all participants are informed and agree to recording. Typically, this can be managed by notifying participants at the start of a call and obtaining either verbal or written consent. This approach meets compliance standards, fosters transparency, and builds trust among participants.
International Context of Consent Laws
Recording laws can also differ significantly on an international level. For example, Canada follows a combination of federal and provincial laws, where most provinces adopt one-party consent. In contrast, in the European Union, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) emphasizes privacy rights, making consent a critical factor in recording personal data, which includes audio or video recordings.
Understanding these legal distinctions is crucial, particularly for global companies and teams. When using AI-powered meeting tools, it’s advisable to limit recordings to instances where everyone is informed and comfortable with them, no matter the jurisdiction. This approach not only builds trust but can also protect companies from complex international legal issues.
Leveraging AI Meeting Tools Responsibly
As technology evolves, AI meeting tools offer features beyond simple recordings. Modern AI tools can provide real-time transcription, noise cancellation, and even generate meeting summaries, making reviewing and sharing essential information easier without storing the entire conversation. Here are some powerful features of AI meeting tools that to use responsibly:
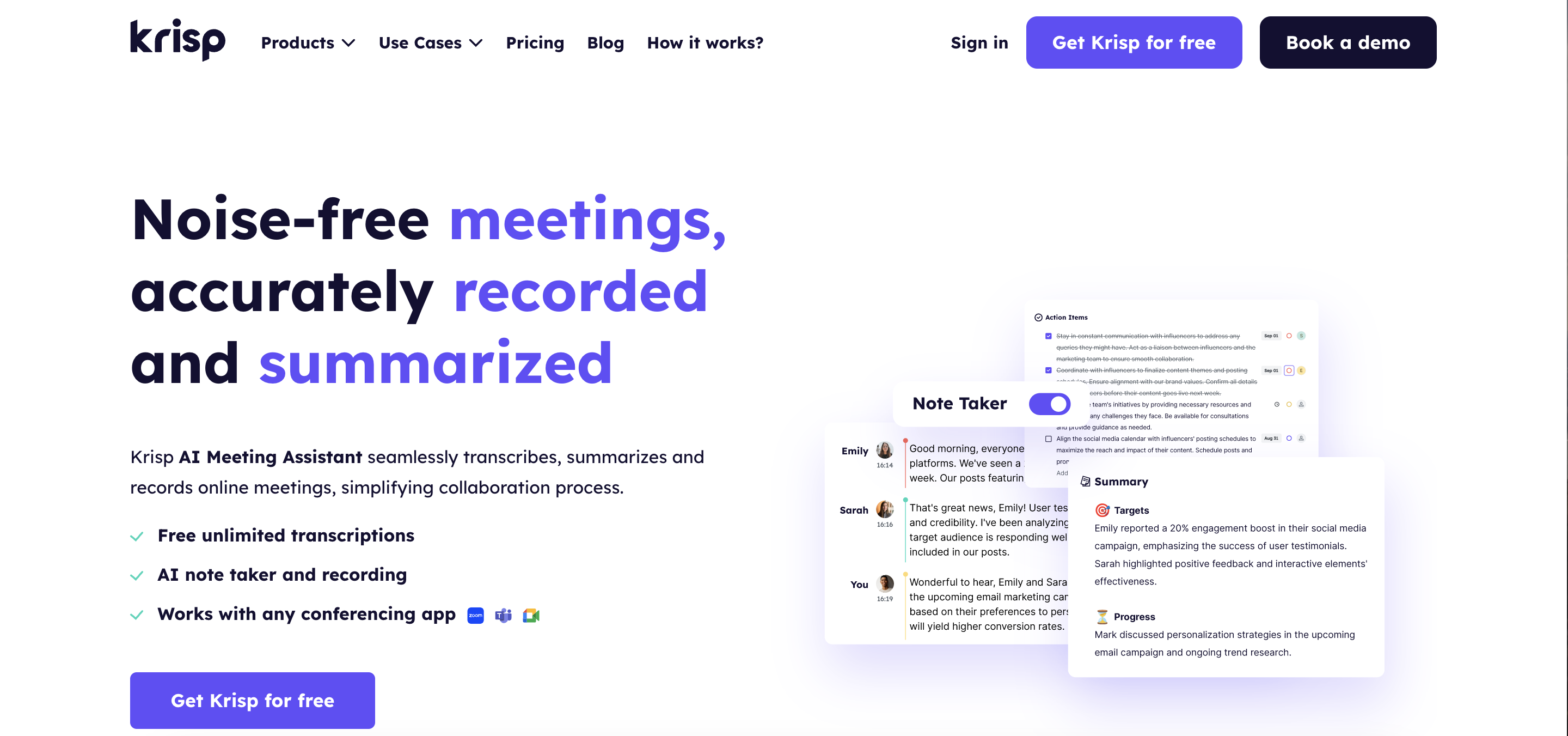
Real-Time Transcription
Noise Cancellation and Voice Filtering
AI meeting tools commonly use noise cancellation to enhance audio quality by filtering out background sounds. For instance, Krisp’s noise cancellation tool leverages AI to reduce distractions, ensuring that only relevant voices come through clearly. This can significantly improve meeting quality, especially for those working in noisy environments.
Noise cancellation is particularly beneficial in fast-paced settings where individuals may not have access to quiet meeting spaces. By using these tools, participants can ensure a professional meeting experience without compromising the quality of information shared.
Automated Summaries and Action Items
Another useful feature in AI meeting tools is the generation of automatic summaries and action items. These tools allow users to capture the essential points of a meeting without storing the full recording. This reduces storage requirements and minimizes potential data privacy risks associated with keeping entire conversations. By focusing on meeting summaries and action items, companies can access valuable insights without compromising participants’ privacy.
In practice, using summaries is highly effective for project updates, brainstorming sessions, and client meetings where detailed records are needed but sensitive information should be minimized.
Selective Recording
With AI meeting tools, selective recording enables users to record only specific segments of a meeting, ensuring that unnecessary parts aren’t stored. This feature can be invaluable for teams looking to balance productivity with privacy. For instance, if only the beginning of a meeting includes critical project details, selective recording can capture that part while avoiding the need to store the entire conversation.
This approach is especially useful in compliance-focused industries, such as finance and healthcare, where retaining only necessary information helps meet regulatory requirements while respecting individual privacy.
When Recording Without Consent is Illegal
Despite the advantages of AI meeting tools, recording someone without their consent can still lead to legal and professional consequences:
- Legal Penalties: In two-party consent jurisdictions, recording without consent violates privacy laws and can result in significant fines or, in serious cases, criminal charges. For instance, in California, unauthorized recording can lead to both civil and criminal penalties. A violation of Penal Code § 632 may lead to a fine of up to $2,500 and/or imprisonment for up to a year (misdemeanor).
- Professional Repercussions: Recording without consent in a workplace setting can damage relationships and trust within teams, as well as harm a company’s reputation. Transparency regarding meeting recordings is essential for maintaining a positive work culture and avoiding potential legal conflicts.
Ethical Considerations: Beyond Legal Compliance
Even when recording is legally permissible, ethical considerations play a significant role in fostering a respectful, trustworthy environment. Here are some ethical aspects to consider:
Transparency and Respect
Ethically, all participants should be aware when a meeting is being recorded. While one-party consent laws may legally permit recording without notification, transparency supports a culture of respect and collaboration. Informing participants promotes trust and encourages open communication, which is particularly important for teams working remotely or across international borders.
Data Security and Confidentiality
Recordings may contain sensitive or confidential information, making data security paramount. Storing entire conversations increases the risk of data breaches, especially in professional settings that involve confidential client or business data. Choosing tools that focus on summaries or selective recordings, like automated action items, helps reduce data storage needs. This approach also minimizes the risks associated with long-term data retention.
Balancing Productivity with Privacy
AI tools such as noise cancellation and transcription can greatly enhance productivity, but it’s essential to use them in ways that respect participants’ privacy. Rather than storing full transcriptions, consider using automated summaries, which keep essential information accessible while maintaining data security.
Best Practices for Responsible Use of AI Meeting Tools
To ensure compliance with legal and ethical guidelines, here are some recommended practices when using AI meeting tools:
- Communicate Recording Intentions Clearly: Inform participants before recording or transcribing. This builds trust and ensures compliance with both one-party and two-party consent requirements.
- Limit Data Storage and Access: Retain only necessary data, such as meeting summaries, rather than entire recordings. This practice minimizes storage needs and potential privacy risks.
- Adjust Features Based on Meeting Needs: Not all meetings require full transcription or recording. Adjust AI meeting tools to match the specific needs of each meeting, balancing productivity with privacy.
- Stay Updated on Recording Laws: Laws around consent can change over time. Staying current with local and international regulations is essential for compliant AI meeting tool use.
- Promote Ethical Use Across Teams: Establish clear guidelines that promote transparency and respect in meeting recordings. Encourage a culture where team members feel comfortable asking questions about recording policies.


