Traditional organizations often expect employees to conform to specific roles or personas, limiting individual expression at work. In contrast, future-oriented organizations value emotional and personal authenticity. Here, employees are encouraged to showcase not only their professional skills but also their emotional and creative sides. This openness fosters a work environment where people feel valued and engaged, enhancing trust and creating room for fresh ideas, innovation, and effective problem-solving.
One of the most transformative—and challenging—aspects of this model is self-management. Unlike the traditional top-down approach, self-managed teams have the authority to make decisions independently. By empowering employees to decide for themselves, these teams can reduce bureaucracy and increase ownership over their work.
In practice, self-management often means decisions are made by those closest to the issue, rather than by managers who may lack direct insight. This approach not only accelerates decision-making but also makes employees feel more connected to the outcomes of their work. This article explores why self-managed teams are poised to shape the future of work and examines the benefits, challenges, and strategies that can help organizations thrive in this model.
What Are Self-Managed Teams?

A self-managed individual operates with full autonomy, meaning they’re not directed by a supervisor or authority figure in their daily actions, processes, or outcomes. They take charge of their work, setting priorities and making decisions that directly influence their results. Self-management requires a high degree of responsibility, discipline, and an understanding of the big-picture goals. These individuals are not only accountable for their own productivity but also for ensuring that their work aligns with organizational objectives.
In the workplace, a self-managed team is a group of employees who come together to achieve a specific project or outcome without direct supervision from a manager or boss. Instead of relying on a top-down approach, self-managed teams function through shared decision-making, where responsibilities are distributed based on team members’ strengths and expertise. They collaborate to set goals, define their approach, and monitor their progress, creating an environment where each team member feels accountable for the team’s overall success. This collective accountability fosters a sense of ownership, which is often linked to higher job satisfaction, motivation, and engagement.
While many organizations operate on traditional management structures, self-management is becoming more common. For instance, seasoned employees—those who know their tasks and roles well—are often trusted to work independently without the need for constant oversight. These individuals may set their own schedules, manage their time efficiently, and report results without needing to be micromanaged. However, even with this degree of autonomy, most employees still check in with a team lead or supervisor periodically for direction, feedback, or alignment with company goals. This approach allows for autonomy while ensuring that everyone remains on track and aligned with the organization’s objectives.
Key Benefits of Self-Managed Teams
Transitioning to self-management doesn’t happen overnight. It takes time, patience, and plenty of communication. But with some effort and refinement, self-management can bring great benefits.
By giving teams and individuals the freedom to manage their own work, you’ll start to see advantages like increased accountability, improved problem-solving, and stronger team engagement. While it may require an adjustment period, the positive outcomes make the process worthwhile.
Self-managed teams can empower employees to take ownership of their roles, boost morale, and help everyone work more effectively toward shared goals.
Greater Employee Engagement
Self-managed teams actively involve everyone in decision-making, not just a few leaders. When team members have a say in business decisions, they’re usually more invested in the outcomes. Plus, by encouraging participation from all team members, self-managed teams make everyone feel like a valuable part of the process.
Less Oversight
Self-managed teams mean less hands-on supervision. This is a big win for employees who enjoy working independently. For instance, if the founder of a local marketing company creates a self-managed team to run social media strategies, they won’t need to sit in on every meeting. This frees up their time to focus on other priorities, like attracting new clients.
Reduced Costs
In larger companies, self-managed teams can help cut costs by reducing the need for extra managers. Fewer managers mean more funds that the company can invest elsewhere, like on new projects or resources that benefit the team.
Better Decision-Making
With self-managed teams, you get insights from the whole group. Since everyone’s voice matters, team members feel comfortable sharing their perspectives. For example, one person might bring up a concern others hadn’t thought of, helping the team make better-informed choices.
Disadvantages of self-managed teams
When thinking about self-managed teams for your organization, it’s good to know the potential downsides so you can tackle them head-on. Here are some challenges of self-managed teams and ideas to address them.
Longer Decision-Making Process
Decisions usually take longer in groups than when made individually. So, when a self-managed team is responsible for making decisions, it might take more time to reach an agreement. This can be an issue when quick decisions are essential. One solution? Self-managed teams can create faster decision-making systems, like a simple voting process, to speed things up.
Need for Self-Motivated Employees
For a self-managed team to thrive, it needs members who are self-motivated and can work well with others. But not every group of employees naturally fits this profile. If the current team isn’t ideal for self-management, there are a couple of options: either hire new members with the right skills or train existing employees to succeed in a self-managed environment.
Limited Innovation
Sometimes, self-managed teams with like-minded members might struggle to think outside the box. For example, if a team creates a successful product, they may stick with similar ideas rather than trying something fresh that customers might want. To prevent this, companies can mix things up by adding more diverse perspectives or rotating team members in and out.
Strategies for Building Self-Managed Teams

Building self-managed teams can transform how an organization operates, promoting autonomy, accountability, and engagement among team members. However, setting up a self-managed team requires more than simply removing a supervisor. It involves creating an environment where team members can communicate effectively, trust one another, and have the right tools and guidance to succeed independently. Here are some key strategies to help organizations build and support successful self-managed teams, fostering both individual growth and collective achievement.
Offer Initial Guidance
Although self-managed teams run themselves, a little guidance at the start can make a big difference. Try giving them a few clear goals and some suggested best practices. As they get into the flow of their work, they can adjust their processes to suit their style, and you can gradually step back.
Start with Team-Building Activities
For self-managed teams to work well, strong communication and trust are key. If you’re forming a new team, consider some team-building activities to help members connect. These exercises help team members get to know each other better, making communication smoother and more comfortable down the line.
Enhance Communication Tools
Once your self-managed team starts working, look for tools they may need to communicate effectively. If your team shares an office, you could designate a specific space for team meetings. For remote teams, consider adding communication software to help them stay connected and collaborate easily.
Regularly Review Team Performance
It’s helpful to review team performance over time to make sure they’re meeting project goals. To support improvement, you can suggest ways to enhance their workflows or communication. Depending on the project size, check in every few weeks or months. When teams consistently perform well, reinforce their success with positive feedback or incentives to keep up the momentum.
How Krisp Helps Self-Managed Teams?
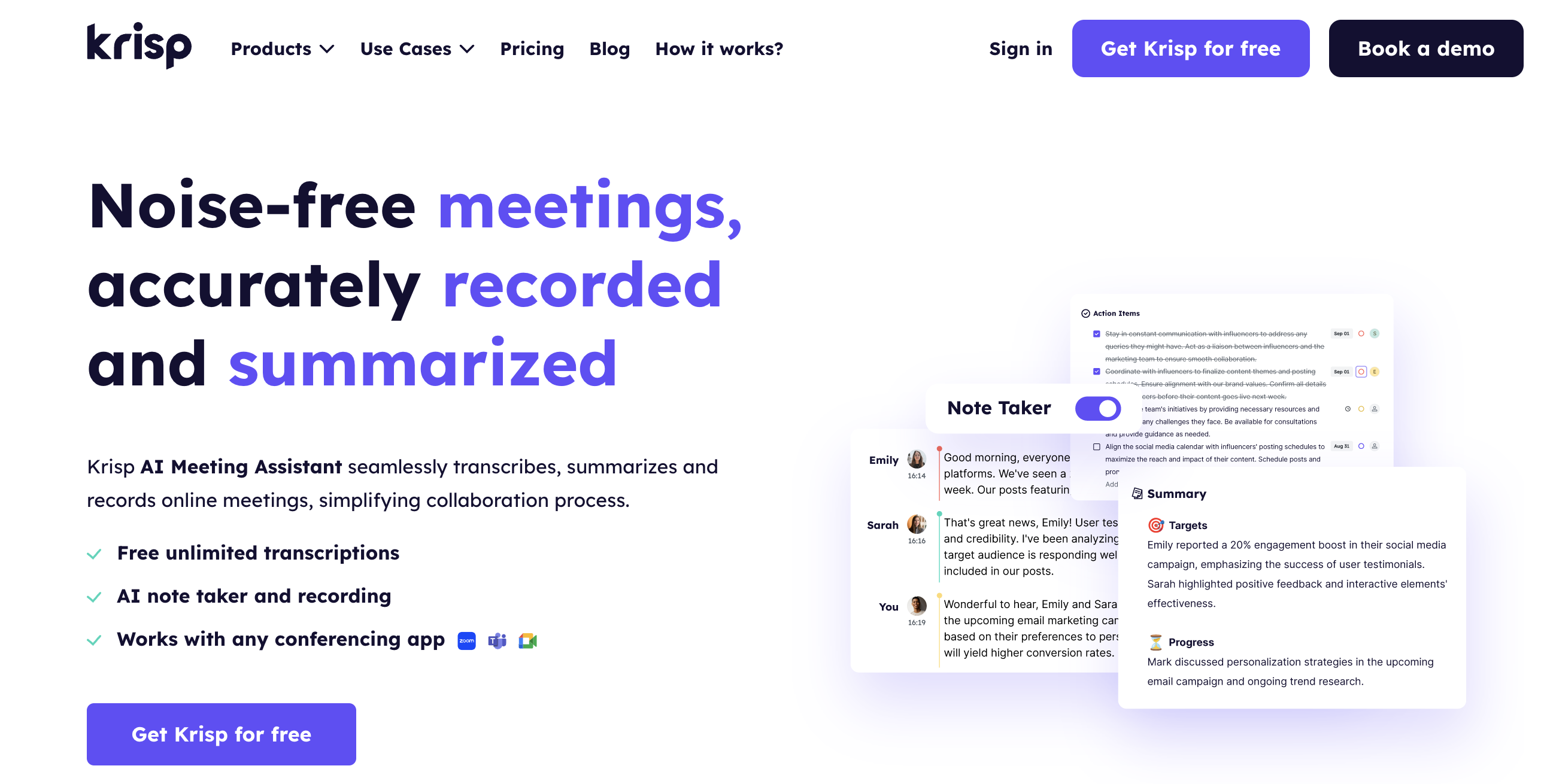
Krisp is an ideal tool for self-managed teams, enhancing communication, focus, and productivity. Here’s how it supports these teams:
- Noise Reduction: Krisp’s AI-driven noise cancellation blocks background noise on both ends of a call, enabling clearer conversations in any environment. This is essential for self-managed teams who often work remotely or in co-working spaces where background noise can be an issue.
- Echo Cancellation: By canceling echo, Krisp ensures that voices come through clearly, reducing distractions and improving communication quality. This feature is especially useful when team members join calls from different types of spaces or devices.
- Meeting Insights: Krisp offers features like real-time transcription and speaker analytics, helping team members focus on what’s being said rather than taking extensive notes. This allows for efficient documentation, making follow-up and information-sharing easier in self-managed settings.
- Cross-Platform Functionality: Krisp works with most conferencing apps, ensuring that teams can use it regardless of the platform. This flexibility is key for self-managed teams that often switch between multiple tools.
- Productivity Boost: By eliminating noise distractions and enabling clear communication, Krisp helps team members stay engaged and productive, which is essential for teams that rely on self-discipline and independence.
- Flexible Subscription Plans: Krisp’s scalable plans make it accessible for teams of all sizes, allowing them to choose the best option for their needs and budget, whether the team is small or growing.
For self-managed teams, Krisp reduces friction in communication and allows members to focus on their work, enabling a more efficient and distraction-free working environment.
Why Self-Managed Teams Are the Future of Work?
Self-managed teams are changing the way organizations get things done, and it all comes down to the power of commitment. In these teams, progress happens through the promises that team members make to each other, not through orders from the top. This setup creates a strong sense of responsibility, where everyone is accountable not just for their own work, but also for the team’s success. When team members feel this commitment, they’re more motivated to jump in and contribute to the group’s goals, leading to faster progress and more innovation.
Even though it might sound odd, leadership is still important in self-managed teams, just in a different way. Instead of being traditional managers who tell everyone what to do, team leaders here act more like guides. They mentor team members, help with team-building, and keep everyone focused on the common vision. This style promotes collaboration over control, allowing team members to own their decisions while still working toward the same objectives. So, while leaders need solid management skills, the focus shifts from calling the shots to being of service to the team.
For self-managed teams to thrive, it’s essential to have a clear vision and set goals. This is even more critical when there isn’t a traditional management structure to provide direction. Teams need to establish clear objectives that align with the organization’s mission, helping members make informed decisions. When everyone understands the shared vision, they can tackle challenges together and come up with innovative solutions, creating a trusting and open atmosphere.
self-managed teams are paving the way for the future of work by harnessing the power of teamwork and shared leadership. As organizations look for more agility and adaptability in a fast-changing world, these teams offer a solid model for long-term success. By empowering individuals, redefining leadership roles, and setting clear goals, self-managed teams not only boost productivity but also create a more engaged and motivated workforce. In a time when collaboration and innovation are key, embracing self-management could be the secret sauce for thriving in the workplace of tomorrow.
FAQ
Increased accountability and ownership among team members.
Enhanced creativity and innovation due to diverse input.
Greater flexibility and adaptability to changes.
Disadvantages:
Potential for conflict if roles and responsibilities aren’t clear.
Risk of decision paralysis if consensus is hard to reach.
Requires strong communication skills and a shared vision to succeed


