Imagine starting a project with a clear goal in mind but no structured plan to get there. You might have a talented team and great ideas, but without a roadmap, progress can quickly become chaotic. This is where sprint planning comes into play.
Sprint planning helps Agile teams set priorities, break work into tasks, and align everyone toward a shared goal. It’s like mapping a journey before starting—you choose the destination, plan the route, and set milestones. This article covers sprint planning fundamentals, its importance, and how to do it effectively.
What is Sprint planning?
Sprint planning is a collaborative event within the Scrum framework where the entire Scrum team—comprising the Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Developers—comes together to determine the work to be accomplished in the upcoming sprint. This meeting sets the stage for the sprint by establishing a clear plan and defining a shared goal.
During sprint planning, the team addresses three primary topics:
- Why is this Sprint valuable? The Product Owner proposes how the product could increase its value and utility in the current sprint. The whole Scrum Team then collaborates to define a Sprint Goal that communicates why the Sprint is valuable to stakeholders. The Sprint Goal must be finalized prior to the end of Sprint Planning.
- What can be done this Sprint? Through discussion with the Product Owner, the Developers select items from the Product Backlog to include in the current Sprint. The Scrum Team may refine these items during this process, which increases understanding and confidence. Selecting how much can be completed within a Sprint is hard. However, the more the Developers know about their past performance, their upcoming capacity, and their Definition of Done, the more confident they will be in their Sprint forecasts.
- How will the chosen work get done? For each selected Product Backlog item, the Developers plan the work necessary to create an Increment that meets the Definition of Done. This is often done by decomposing Product Backlog items into smaller work items of one day or less. How this is done is at the sole discretion of the Developers. No one else tells them how to turn Product Backlog items into Increments of value.
By thoroughly engaging in sprint planning, the Scrum team ensures alignment on objectives, fosters a clear understanding of tasks, and sets a focused direction for the sprint ahead.
Who Needs Sprint Planning?
Sprint planning serves as a fundamental component of the Scrum framework, which is widely adopted by agile teams to manage complex projects. During sprint planning, the Scrum team—including the Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team—decides on the work for the next sprint. This collaboration ensures alignment on objectives, priorities, and commitments to backlog items. Sprint planning improves communication, clarifies goals, and helps teams deliver valuable product increments efficiently.
Where Is Sprint Planning Used?
Sprint planning, a cornerstone of the Scrum framework, has transcended its origins in software development and found applications across various industries. In education, universities have adopted Scrum techniques to enhance collaboration among departments, thereby increasing organization and effectiveness. In the construction sector, companies have implemented Agile methodologies to manage high capital risks and stringent schedules, enabling real-time decision-making and effective communication.
The automotive industry has also embraced Scrum to accelerate innovation, moving away from traditional, slower development cycles. Marketing and advertising firms utilize Agile methods to improve decision-making and productivity, as exemplified by Teradata Applications, which credits Scrum for enhanced communication and process improvements. Event planning companies benefit from Scrum’s iterative framework, allowing for real-time changes based on feedback, leading to better execution of events. In product development, Agile principles have facilitated rapid prototyping and innovation, with companies like Wikispeed developing functional prototypes in significantly reduced timeframes.
Financial services firms face emerging challenges in technology and risk management, prompting many to adopt Scrum to meet customer expectations. Even military organizations, such as various U.S. military groups, rely on Scrum to coordinate complex operations, where efficient communication is critical.
How to Run Sprint Planning?
Effective sprint planning lays the groundwork for a productive and well-structured sprint, ensuring that teams align their efforts with project goals. This critical meeting brings together key stakeholders, including developers, the Scrum Master, and the Product Owner, to define priorities and establish a clear direction for the upcoming sprint. When conducted properly, sprint planning helps teams maximize efficiency, minimize uncertainties, and create a shared understanding of the tasks ahead. To achieve this, teams must follow a well-defined approach that balances strategy, collaboration, and execution.
Step 1: Review the Product Backlog and Define the Sprint Goal
The process begins with the Product Owner presenting the highest-priority items from the product backlog to the team. These items should meet the team’s criteria for readiness, ensuring they are actionable. The team discusses these items to gain a shared understanding of the requirements and objectives. Based on this discussion, the team collaboratively defines a clear and concise sprint goal that articulates the value, delivering to stakeholders in the upcoming sprint. This goal provides focus and direction, guiding the team’s efforts throughout the sprint.
Step 2: Assess Team Capacity and Select Backlog Items
With the sprint goal set, the team assesses capacity based on availability, past velocity, and other commitments. They choose backlog items that fit the goal and sprint duration. Each item is discussed for clarity, and larger tasks may be broken down. This process ensures a realistic workload, maintaining a sustainable pace and increasing success.
Step 3: Develop a Plan to Achieve the Sprint Goal
After selecting backlog items, the team creates a plan to complete the work efficiently. They identify tasks, estimate effort, and determine dependencies. Tasks may be assigned or self-assigned based on expertise and workload. The plan stays flexible to handle changes and challenges. The sprint backlog, listing tasks and backlog items, guides the team in achieving the sprint goal.
To enhance efficiency during sprint planning and execution, teams can use Krisp AI meeting assistant to capture key discussions, track action points, and ensure alignment among all members. Krisp’s AI-powered note-taking capabilities help teams stay organized by summarizing essential conversations, recording task assignments, and automatically generating insights from meetings. This ensures that no critical information lost, allowing the team to focus on delivering high-value work while minimizing the need for manual documentation.
Best Practices for Sprint Planning
Effective sprint planning serves as a cornerstone for successful agile project management, ensuring that development teams align their efforts with product goals and deliver value consistently. To conduct a productive sprint planning session, teams should adhere to several best practices.
1. Assess Team Capacity
Before finalizing the sprint backlog, the team must assess its capacity to ensure realistic workload distribution. This involves considering factors such as planned absences, team members’ individual commitments, and any external dependencies that could impact availability. Additionally, reviewing historical sprint velocity provides valuable insights into how much work the team can realistically complete within the sprint duration. Sprint velocity helps avoid overcommitment by setting expectations based on actual past performance rather than assumptions. To ensure sustainable productivity, teams should avoid overloading themselves with excessive tasks, as this can lead to burnout, missed deadlines, and decreased quality of work. Instead, they should allocate work in a way that balances efficiency and feasibility while allowing room for unexpected challenges.
2. Collaborate as a Team
Sprint planning should involve all team members actively contributing to discussions to ensure alignment on goals and tasks. Open communication among developers, testers, and product owners fosters a shared understanding of sprint objectives. When everyone knows their roles, the team works more cohesively, improving efficiency and reducing misunderstandings.
Using Krisp AI Meeting Assistant can significantly enhance collaboration in sprint planning, especially for remote or distributed teams. Krisp’s AI-powered features, such as real-time noise cancellation, meeting transcription, and smart note-taking, enable seamless and distraction-free discussions. With automated meeting summaries and action item tracking, teams can ensure that Krisp documented key decisions and commitments, reducing the risk of miscommunication. Additionally, Krisp allows asynchronous collaboration by providing searchable transcripts, enabling team members who couldn’t attend the meeting to stay updated and contribute effectively.
Integrating Krisp into sprint planning improves engagement, ensures clear communication, and captures valuable insights accurately. This creates a more inclusive and productive process where every team member feels valued, informed, and aligned with sprint goals.
3. Time-Box the Planning Meeting
To stay efficient and prevent delays, sprint planning has time-box based on the sprint length. A common practice is allocating two hours of planning per sprint week, so a two-week sprint gets four hours. Sticking to a set time frame keeps discussions focused and avoids unnecessary delays. A structured agenda with clear goals and prepared backlog items boosts productivity. Keeping planning concise yet thorough helps teams stay on track while making essential decisions within the set time.
4. Consider Feedback from Previous Sprints
A successful sprint planning process incorporates lessons learned from previous sprints to continuously improve efficiency and team performance. Reviewing retrospective insights helps teams identify recurring issues, areas for improvement, and best practices. By addressing challenges from past sprints, teams can proactively implement strategies to mitigate potential risks in future iterations. Whether it’s adjusting workload distribution, refining estimation techniques, or improving collaboration dynamics, applying these learnings enhances overall workflow. Regularly integrating retrospective feedback into sprint planning ensures that the team evolves, refines its processes, and consistently delivers high-quality results.
FAQ
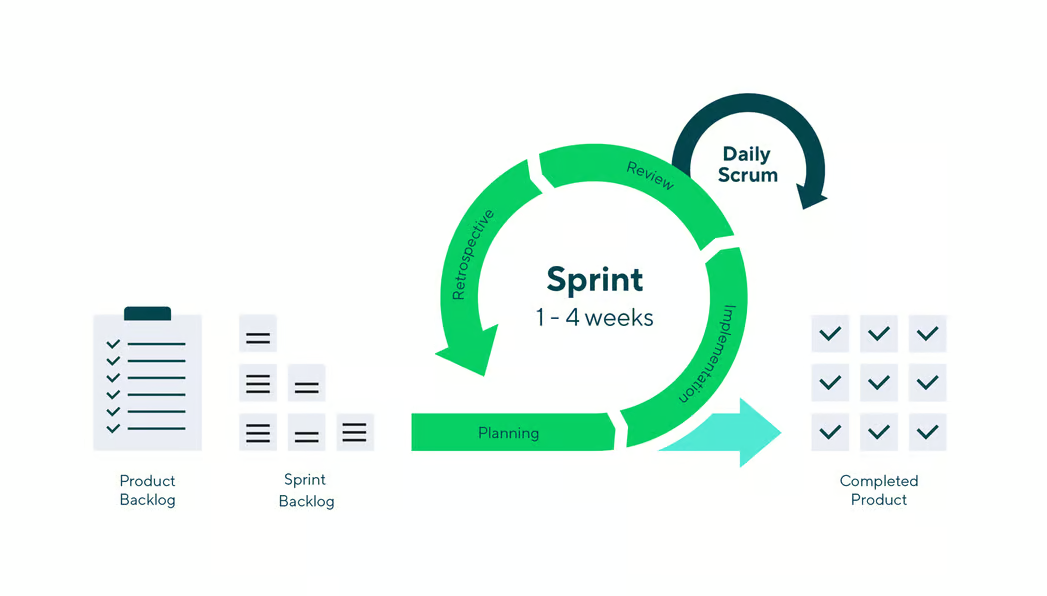
1. Sprint Planning – The team defines the sprint goal, selects backlog items, and creates a work plan.
2. Daily Scrum – A short daily stand-up to discuss progress, challenges, and next steps.
3. Development Work – The team develops, tests, and refines features collaboratively.
4. Sprint Review – The team presents completed work to stakeholders for feedback and validation.
5. Sprint Retrospective – A reflection on successes, areas for improvement, and future sprint optimizations.


